BD Micro
SKU: 37543
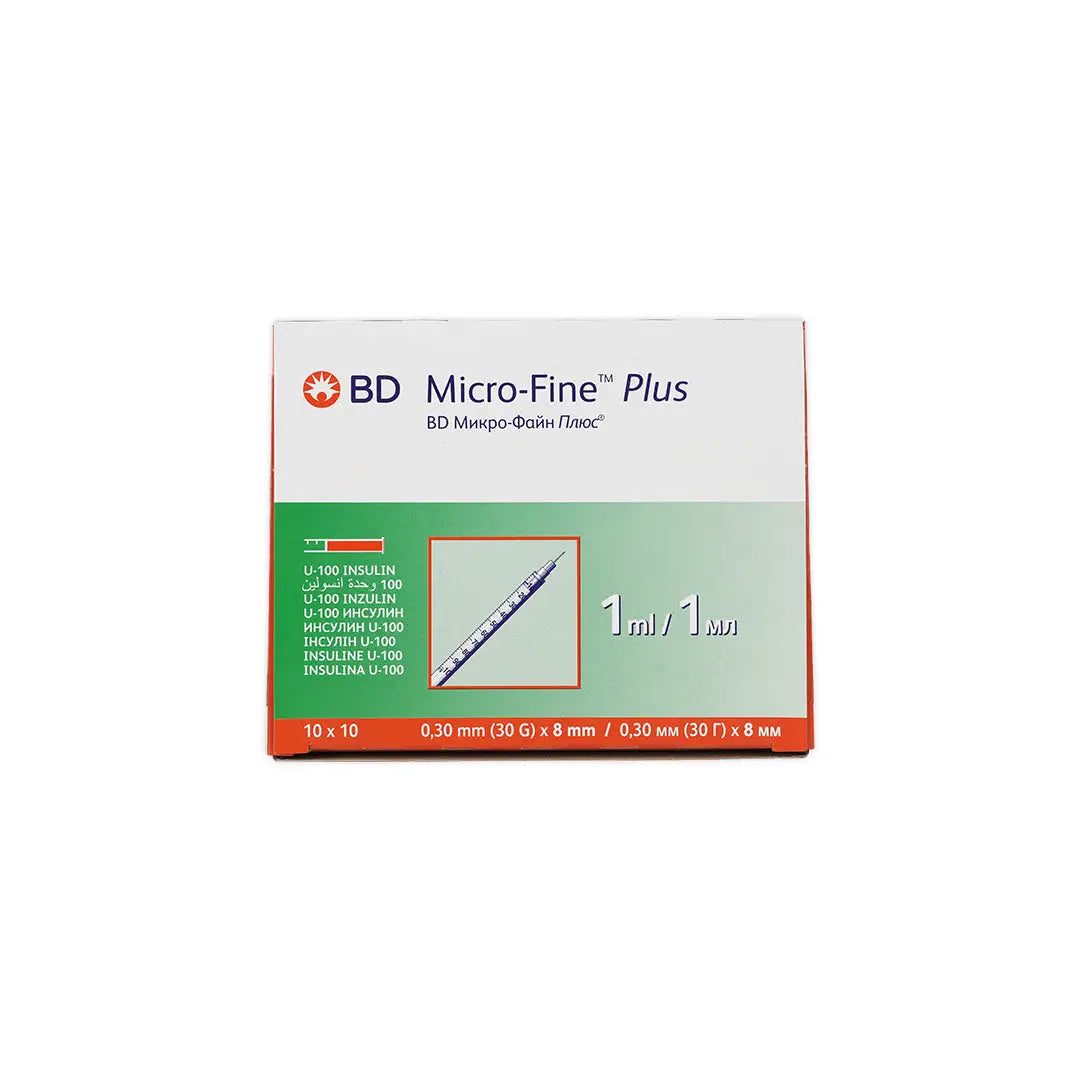
This syringe provides an excellent option for regular insulin administration, offering a quick, easy, and secure method for precise glycemic control. The lubricated syringes enhance injection quality and reduce discomfort, while the sharp-edged needles penetrate the skin effortlessly, minimizing pain.
Benefits:
-The 1ml capacity allows for accurate measurement of small doses, which is crucial for medications like insulin.
-The 30G (gauge) needle is thinner than standard needles, which minimizes discomfort during injection and reduces tissue trauma.
- The 8mm length is ideal for subcutaneous injections, ensuring that the medication is delivered into the correct layer of tissue without penetrating too deeply.
-Designed for self-administration, these syringes often come with features such as easy-to-read markings and a comfortable grip.
Sterility: Each syringe is individually packaged to maintain sterility until use, reducing the risk of infection.
Main Ingredients & Their Benefits:
-Polypropylene (PP) is a thermoplastic polymer used to manufacture the barrel and plunger of the syringe. Polypropylene is known for its durability, chemical resistance, and low moisture absorption. It ensures that the syringe maintains its integrity during storage and use.
-Rubber is typically used in the plunger tip to create a seal that prevents leakage of medication. The elasticity of rubber allows for smooth movement of the plunger while providing an airtight seal.
-Silicone oil may be used as a lubricant on the inner surface of the syringe barrel to facilitate smooth plunger movement. This reduces friction during injection, making it easier for users to administer medication accurately.
Benefits:
-The 1ml capacity allows for accurate measurement of small doses, which is crucial for medications like insulin.
-The 30G (gauge) needle is thinner than standard needles, which minimizes discomfort during injection and reduces tissue trauma.
- The 8mm length is ideal for subcutaneous injections, ensuring that the medication is delivered into the correct layer of tissue without penetrating too deeply.
-Designed for self-administration, these syringes often come with features such as easy-to-read markings and a comfortable grip.
Sterility: Each syringe is individually packaged to maintain sterility until use, reducing the risk of infection.
Main Ingredients & Their Benefits:
-Polypropylene (PP) is a thermoplastic polymer used to manufacture the barrel and plunger of the syringe. Polypropylene is known for its durability, chemical resistance, and low moisture absorption. It ensures that the syringe maintains its integrity during storage and use.
-Rubber is typically used in the plunger tip to create a seal that prevents leakage of medication. The elasticity of rubber allows for smooth movement of the plunger while providing an airtight seal.
-Silicone oil may be used as a lubricant on the inner surface of the syringe barrel to facilitate smooth plunger movement. This reduces friction during injection, making it easier for users to administer medication accurately.
-Polypropylene (PP). -Rubber (Natural or Synthetic). -Silicone Oil (Coating)
Recently Viewed